涼拌小黃黄瓜 liángbàn xiǎohuángguā Cold cucumber is a light and refreshing Taiwanese side dish that’s perfect for hot summer days. Made with crunchy cucumbers, sugar, salt, vinegar, garlic, and a hint of chili, it strikes the perfect balance of tangy, savory, and slightly spicy flavors. The cucumbers are lightly smashed to soak up the marinade, and…
Author: tiffany
“May as well” in Chinese – 也好 yěhǎo
Grammar Point:The Chinese phrase 也好 yěhǎo can mean “may as well” or “it’s fine either way”, depending on the context. Structure Option 1 + 也好 yěhǎo,Option 2 + 也好 yěhǎo This usage indicates that the speaker is indifferent or finds either option acceptable. It’s often used in casual, conversational contexts. 你nǐ去qù也好yěhǎo, 不bú去qù也好yěhǎo, 隨便suíbiàn你nǐ你nǐ去qù也好yěhǎo, 不bú去qù也好yěhǎo, 随便suíbiàn你nǐYou may as well go or…
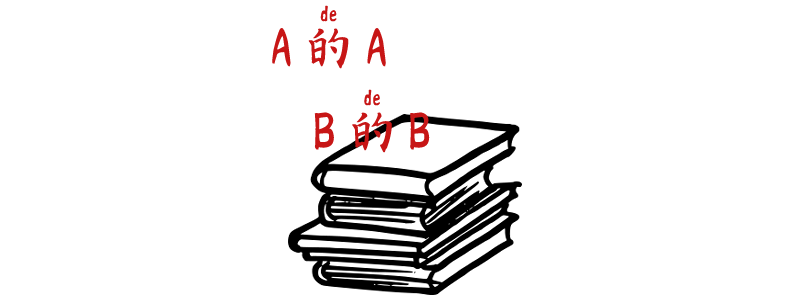
A 的 de A,B 的 de B
Grammar Point:The colloquial pattern is used to describe a situation where each person or thing has its own characteristic, role, or condition. It emphasizes the individuality or diversity within a group, often giving a sense of balance, division, or order. Structure A 的 de A,B 的 de B A refers to one group or condition,…
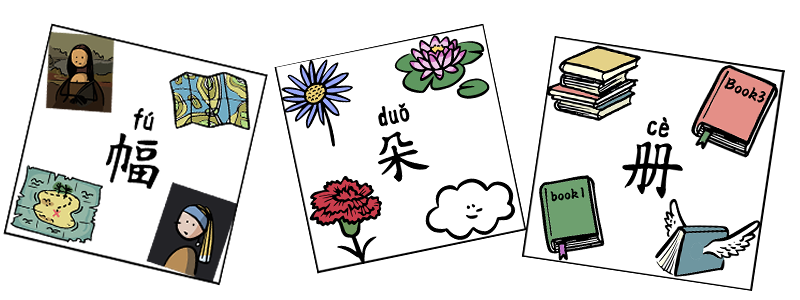
Chinese Measure Words 5
Grammar Point:In this article, we are going to introduce the following Chinese measure words: 册 cè, 朵 duǒ, 幅 fú, 屆届 jiè, 顆顆 kē, 匹 pī, 扇 shàn 册 (cè) This is a measure word in Chinese used to indicate a collection of written or printed materials, such as books, albums, or bound volumes. It is commonly used when referring to…
Adverbs of Frequency 2
Grammar Point:In Chinese, words like 時时刻 shíkè, 時时常 shícháng, 偶爾尔 ǒu’ěr, and 不時时 bùshí are essential for expressing time-related concepts and the frequency of actions or events. Structure – Adverbs of Frequency + Verb 時时刻 shíkè 時时刻 shíkè means “constantly” or “at all times.” It highlights a continuous state or consistent attention, often appearing in formal or serious contexts. 中文zhōngwén老師lǎoshī時刻shíkè準備zhǔnbèi找zhǎo出chū你nǐ說shuō錯cuò的de中文zhōngwén中文zhōngwén老师lǎoshī时刻shíkè准备zhǔnbèi找zhǎo出chū你nǐ说shuō错cuò的de中文zhōngwénChinese teachers…
Express “along with” in Chinese – suízhe
Grammar Point:The Chinese word 隨著随着 suízhe means “along with,” “following,” or “as… happens.” It is a preposition commonly used to indicate changes, developments, or events occurring simultaneously with something else. Structure S + 隨著随着 suízhe + Noun + Verb Phrase 大家dàjiā隨著suízhe音樂yīnyuè開始kāishǐ跳舞tiàowǔ大家dàjiā随着suízhe音乐yīnyuè开始kāishǐ跳舞tiàowǔEveryone started dancing to the music. 我們wǒmen隨著suízhe導遊dǎoyóu走zǒu進jìn了le古老gǔlǎo的de城堡chéngbǎo我们wǒmen随着suízhe导游dǎoyóu走zǒu进jìn了le古老gǔlǎo的de城堡chéngbǎoWe followed the guide into the ancient castle. 狗狗gǒugǒu隨著suízhe主人zhǔrén的de聲音shēngyìn跑pǎo過guò來lái了le狗狗gǒugǒu随着suízhe主人zhǔrén的de声音shēngyìn跑pǎo过guò来lái了leThe dog ran…
“Mostly” in Chinese – 大都 dàdōu
Grammar Point:大都 dàdōu is an adverb in Chinese that means “mostly” or “for the most part.” It is used to describe situations, actions, or characteristics that are true in general but may have exceptions. Structure S + 大都 dàdōu + Auxiliary Verb or Verb 他們tāmen大都dàdōu會huì去qù參加cānjiā這zhè次cì活動huódòng他们tāmen大都dàdōu会huì去qù参加cānjiā这zhè次cì活动huódòngMost of them will attend this event. 你nǐ講jiǎng的de話huà他tā大都dàdōu沒méi在zài聽tīng你nǐ讲jiǎng的de话huà他tā大都dàdōu没méi在zài听tīngHe hardly listens to what you say. 這個zhège季節jìjié的de水果shuǐguǒ大都dàdōu很hěn新鮮xīnxiān这个zhège季节jìjié的de水果shuǐguǒ大都dàdōu很hěn新鲜xīnxiānMost of…
“Simply” in Chinese 2 – 干脆 gāncuì
Grammar Point:The Chinese word 乾干脆 gāncuì is often used in conversational or informal contexts to express decisiveness or simplicity. It can sometimes convey a tone of impatience, encouraging someone to stop overcomplicating things. In English, it is often translated as “simply” or “just.” Structure S + 乾干脆 gāncuì + Verb/Clause When 乾干脆 gāncuì is used as an adverb, it emphasizes a…
“According to” in Chinese 3 – yīzhào and yījù
Grammar Point:The Chinese words 依照 yīzhào and 依據据 yījù both mean “according to” or “based on,” and they are often used to indicate that an action, decision, or judgment is being made following a standard, rule, evidence, or guideline. 依照 yīzhào It often used in situations involving practical actions or processes, where instructions or methods are explicitly stated. 依照yīzhào說明書shuōmíngshū安裝ānzhuāng依照yīzhào说明书shuōmíngshū安装ānzhuāngInstall…
“Secretly” in Chinese – 偷偷 tōutōu
Grammar Point:偷偷 tōutōu is an adverb in Chinese that means “secretly,” “stealthily,” or “quietly without being noticed.” It describes an action that is done with the intention of avoiding detection or attention. Structure S + 偷偷 tōutōu + (地 de) + V In modern usage, 地 de (a particle that connects adverbs to verbs) can be omitted with 偷偷 tōutōu, especially…