Grammar Point:You can simply translate “由於于 yóuyú” into “due to” in English. It is often used at the beginning of a sentence to introduce the cause or reason for something that has happened. Structure 由於于 yóuyú + cause,effect Unlike the 因為为 yīnwèi, which indicates a direct cause-and-effect relationship between two things, the 由於于 yóuyú structure…
Author: tiffany
Because and so in Chinese – yīnwèi and suǒyǐ
Grammar Point:The word “because” can be expressed as 因為为 yīnwèi in Chinese. While “so” is 所以 suǒyǐ. The structure of 因為为 yīnwèi……所以 suǒy…… is a common Chinese pattern used to express cause-and-effect relationships between two clauses. Structure 因為为 + reason + 所以 + result The pattern of 因為为 yīnwèi (because)⋯所以 suǒyǐ (so)⋯is common in both…
Tone Pair Charts
There are many audio files on this Tone Pair Charts page. If you can’t hear the sound, please wait 10 seconds and try again. Full Chart 1st tone 2nd tone 3rd tone 4th tone 1st tone 🔊 tiānkōng 🔊 yuángōng 🔊 shǒujī 🔊 dàjiā 2nd tone 🔊 zhīzú 🔊 qíngrén 🔊 měiguó 🔊 bàngqiú 3rd…
Japanese Food
Kitchen Food Japanese Simplified China Traditional Taiwan English 天ぷら 天妇罗 tiānfùluó 天婦羅 tiānfùluó Tempura らーめん 拉面 lāmiàn 拉麵 lāmiàn Ramen うどん 乌冬面 wūdōngmiàn 烏龍麵 wūlóngmiàn Udon 牛丼 牛肉盖饭 niúròu gàifàn 牛肉蓋飯 niúròu gàifàn Gyudon 鰻の蒲焼き 蒲烧鳗鱼 púshāományú 蒲燒鰻 púshāomán Unagi カツ丼 炸猪排盖饭 zházhūpáigàifàn 日式炸豬排飯 rìshì zhàzhūpáifàn katsudon 親子丼 滑蛋鸡肉饭 huádànjīròufàn 親子丼 qīnzǐdòng Oyakodon 焼きそば 日式炒面…
Synonyms of “Always” in Chinese
There are four ways to say “always” in Chinese, and these are the words 總是总是 zǒngshì, 老是 lǎoshì, 一向 yíxiàng and 一直 yìzhí. However, there are subtle differences in the nuances of these words that are worth noting: 總总是 zǒngshì 總是总是 zǒngshì is used to emphasize a high probability or frequency. 他tā上午shàngwǔ八點bādiǎn總是zǒngshì在zài圖書館túshūguǎn看書kànshū他tā上午shàngwǔ八点bādiǎn总是zǒngshì在zài图书馆túshūguǎn看书kànshūHe is always in…
No wonder in Chinese – nánguài & guàibude
Grammar point: Both 難难怪 nánguài and 怪不得 guàibùdébude mean “no wonder” or “it’s no surprise.” It is used to express realization or understanding of why something happens, often after discovering new information or reasoning behind it. It can also convey agreement with a logical conclusion. Structure 難难怪 nánguài + Observation + 原來来 yuánlái (是 shì) + The…
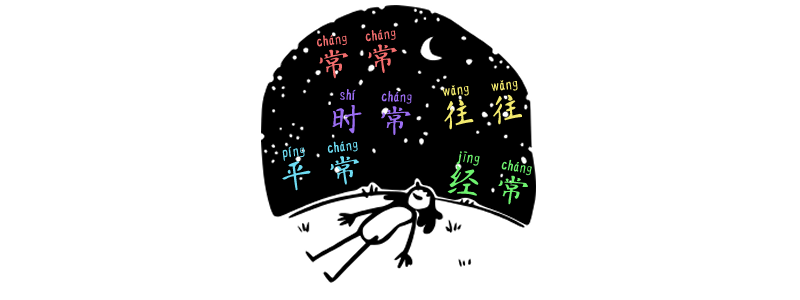
Synonym of Often in Chinese
Introduction:常常 chángcháng, 經常经常 jīngcháng, 往往 wǎngwǎng, 平常 píngcháng, and 時常时常 shícháng share a similar meaning of “often” or “frequently,” but there are some differences in their usages and connotations. 常(常) cháng(cháng) Adverb 常(常) cháng(cháng) means “often” and is always interchangeably with 經常经常 jīngcháng. However, it can sometimes imply a slightly more casual or less frequent…
Adverbs of Frequency 1
Chinese adverbs of frequency are words that indicate how often an action occurs. Some common Chinese adverbs of frequency include: Structure Adverbs of Frequency + Verb It’s important to note that Chinese adverbs of frequency can appear before or after the verb they modify, but they generally appear before the adverbs of manner in a…
10 Drinks in Taiwan and China
Here are 10 drinks in Taiwan and China, some of them might be weird for you, but I still recommend you try them at least once. 1. Bubble Milk Tea (珍珠奶茶 zhēnzhū nǎichá) Bubble tea, also known as boba tea, pearl milk tea, or simply boba, is a Taiwanese tea-based drink that has become popular…
Chinese Measure Words 3
Grammar Point:In this article, we are going to introduce the following Chinese measure words: 把 bǎ, 行 háng, 架 jià, 群 qún, 束 shù, 台 tái, 家 jiā, 頁页 yè 把 (bǎ) This is a measure word in Chinese that is used to indicate a group of objects or one certain object that can be held with one hand, such…