Grammar Point:趁 chèn is a preposition or verb meaning to take advantage of a time or situation—to do something while conditions are right or before they change.This usage does not translate naturally into English word-for-word and is usually better understood by its function rather than a direct equivalent. Structure 趁 chèn + condition / situation / opportunity…
Author: tiffany
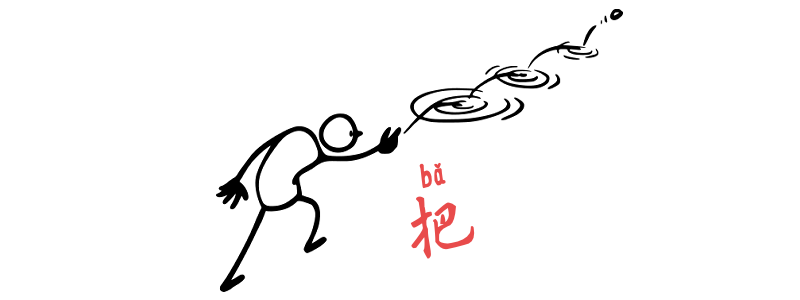
Resultative Complements with 把 bǎ
Grammar Point:把 is used when the speaker wants to: So with 把, the sentence focuses on the result, not just the action. If you’re not familiar with the basic foundation of 把 structure, I suggest reading the following articles first. Structure Things + 把 bǎ + O + Verb + Something 她tā把bǎ杯子bēizi打dǎ破pò了le她tā把bǎ杯子bēizi打dǎ破pò了leShe broke the cup. 你nǐ別bié把bǎ他tā的de東西dōngxī弄nòng壞huài了le你nǐ别bié把bǎ他tā的de东西dōngxi弄nòng坏huài了leDon’t damage…
B2 L9 Vocabulary and Practice
There’s a small menu in the bottom right corner where you can choose how you want to review. Options include:
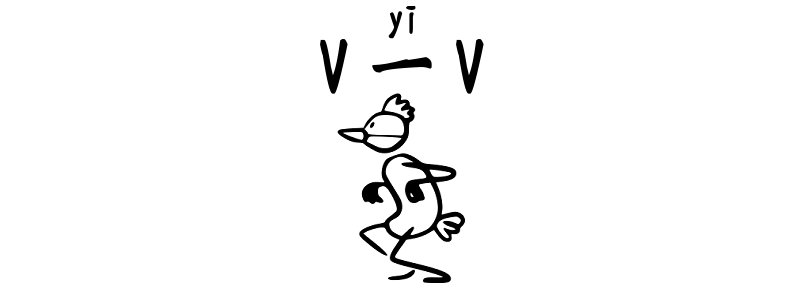
把 bǎ + V (一) V
What is a 把 bǎ sentence? In Chinese, sometimes you want to focus on what you do to something, not just the action. What does “V 一 V” mean? You do the action quickly or lightlyYou are just trying or checkingThe action is small or casual 📌 See more details here Structure 把 bǎ + object + V +…
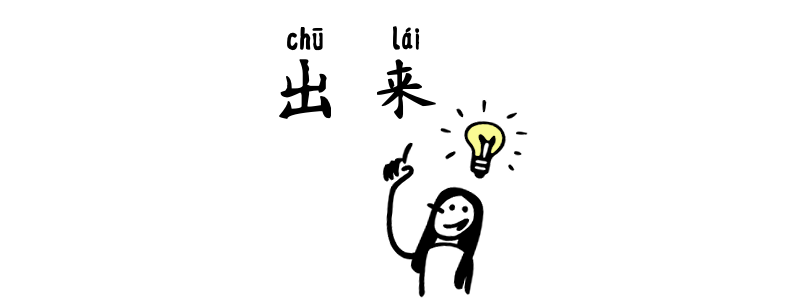
Chinese Complement – 出來 chūlái
What is “出來来 chūlái” ? 出來来 chūlái is a directional + result complement made of: It is added after a verb to show movement, emergence, or a result that becomes visible or perceptible. V + 出(來来) chū(lái) From a hidden state to a revealed state/ to emergence 我wǒ要yào做zuò出chū成績chéngjī我wǒ要yào做zuò出chū成绩chéngjìI need to see some results. 為了wèile做zuò出chū這個zhège網站wǎngzhàn, 我wǒ好hǎo累lèi为了wèile做zuò出chū这个zhège网站wǎngzhàn, 我wǒ好hǎo累lèi 😵💫I am so tired to make this website….
Chinese Complement – 下 xià
Grammar Point:In Chinese, 下 xià can be used as a result/directional complement to show that there is enough space, capacity, or ability to accommodate something. This use is very common in daily spoken Chinese. Structure V + 得 de or 不 bu + 下 xià 我家wǒjiā很hěn小xiǎo, 只zhǐ住得下zhùdexià兩liǎng個ge人rén我家wǒjiā很hěn小xiǎo, 只zhǐ住得下zhùdexià两liǎng个ge人rénMy house is small. It’s only two people can live there. 他的tāde包包bāobāo裝不下zhuāngbúxià5 本běn書shū他的tāde包包bāobāo装不下zhuāngbuxià5…
HSK6 Reading Practice –
HSK6 Reading Practice Remember to use the menu at the top right of the article to switch between Traditional and Simplified Chinese. Vocabulary 歧視qíshì歧视qíshìdiscrimination;to discriminate 他tā覺得juéde自己zìjǐ因為yīnwèi年紀niánjì比較bǐjiào大dà, 在zài找zhǎo工作gōngzuò時shí被bèi歧視qíshì他tā觉得juéde自己zìjǐ因为yīnwèi年纪niánjì比较bǐjiào大dà, 在zài找zhǎo工作gōngzuò时shí被bèi歧视qíshìHe feels he’s being discriminated against in job hunting because of his age. 附和fùhè附和fùhèto agree with; to echo 她tā一yì說shuō完wán,,我wǒ就jiù忍不住rěnbúzhù附和fùhè, 因為yīnwèi我wǒ也yě有yǒu同樣tóngyàng的de感覺gǎnjué她tā一yì说shuō完wán, 我wǒ就jiù忍不住rěnbúzhù附和fùhè, 因为yīnwèi我wǒ也yě有yǒu同样tóngyáng的de感觉gǎnjuéAs soon as she finished speaking, I…
B2 L8 Vocabulary and Practice
There’s a small menu in the bottom right corner where you can choose how you want to review. Options include:
Winter Solstice – 冬至 dōngzhì
Dongzhi 冬至dōngzhì冬至dōngzhì是shì華人huárén文化wénhuà中zhōng一個yíge很hěn重要zhòngyào的de日子rìzi,通常tōngcháng在zài是shì华人huárén文化wénhuà中zhōng一个yíge很hěn重要zhòngyào的de日子rìzi,通常tōngcháng在zài12月yuè21日rì到dào23日rì之間zhījiān12月yuè21日rì到dào23日rì之间zhījiān。這zhè一yì天tiān是shì一年yìnián中zhōng。这zhè一yì天tiān是shì一年yìnián中zhōng白天báitiān最zuì短duǎn、晚上wǎnshàng最zuì長cháng白天báitiān最zuì短duǎn、 晚上wǎnshang最zuì长cháng的de一天yìtiān。從cóng冬至dōngzhì開始kāishǐ,白天báitiān會huì一天yìtiān一天yìtiān變biàn長cháng,代表dàibiǎo的de一天yìtiān。从cóng冬至dōngzhì开始kāishǐ,白天báitiān会huì一天yìtiān一天yìtiān变biàn长cháng,代表dàibiǎo新xīn的de開始kāishǐ和hé希望xīwàng新xīn的de开始kāishǐ和hé希望xīwàng。。 The Winter Solstice, known as Dongzhi 冬至, is one of the most important seasonal festivals in Chinese culture. It usually falls around December 21–23, marking the shortest day and longest night of the year. From this day on, daylight gradually becomes longer, symbolizing renewal, balance, and hope. In China 在zài在zài中國Zhōngguó中国Zhōngguó,人們rénmen覺得juéde冬至dōngzhì是shì一個yíge天氣tiānqì開始kāishǐ慢慢mànmàn變biàn暖nuǎn的de重要zhòngyào時間shíjiān。很hěn多duō家庭jiātíng會huì在zài這zhè一天yìtiān一起yìqǐ吃飯chīfàn,吃chī一些yìxiē可以kěyǐ讓ràng身體shēntǐ變biàn暖nuǎn的de食物shíwù。南方nánfāng的de人rén常cháng吃chī,人们rénmen觉得juéde冬至dōngzhì是shì一个yíge天气tiānqì开始kāishǐ慢慢mànmàn变biàn暖nuǎn的de重要zhòngyào时间shíjiān。很hěn多duō家庭jiātíng会huì在zài这zhè一天yìtiān一起yìqǐ吃饭chīfàn,吃chī一些yìxiē可以kěyǐ让ràng身体shēntǐ变biàn暖nuǎn的de食物shíwù。南方nánfāng的de人rén常cháng吃chī湯圓tāngyuán汤圆tāngyuán,北方běifāng的de人rén則zé常cháng吃chī,北方běifāng的de人rén则zé常cháng吃chī餃子jiǎozi饺子jiǎozi。大家dàjiā相信xiāngxìn,吃chī了le這些zhèxiē食物shíwù,冬天dōngtiān會huì比較bǐjiào不bù容易róngyì生病shēngbìng。。大家dàjiā相信xiāngxìn,吃chī了le这些zhèxiē食物shíwù,冬天dōngtiān会huì比较bǐjiào不bù容易róngyì生病shēngbìng。 In China, Dongzhi has traditionally been seen as a time…
Just like – 像 xiàng… 一樣 yíyàng
Grammar Point:像 xiàng… 一樣样 yíyàng is used to compare two things, meaning “just like,” “as…as,” “the same as.”It shows similarity in appearance, attitude, feeling, or situation. Structure A 像 xiàng B 一樣样 yíyàng + Adj or V Comparing things or people. 台灣Táiwān的de小籠包xiǎolóngbāo像xiàng香港xiānggǎng的de一樣yíyàng好吃hǎochī台湾Táiwān的de小笼包xiǎolóngbāo像xiàng香港xiānggǎng的de一样yíyàng好吃hǎochīTaiwan’s soup dumplings are as delicious as Hong Kong’s. 他tā的de樣子yàngzi就jiù像xiàng明星míngxīng一樣yíyàng帥shuài嗎ma? 他tā的de样子yángzi就jiù像xiàng明星míngxīng一样yíyàng帅shuài吗ma? Does he look as handsome as a celebrity?…